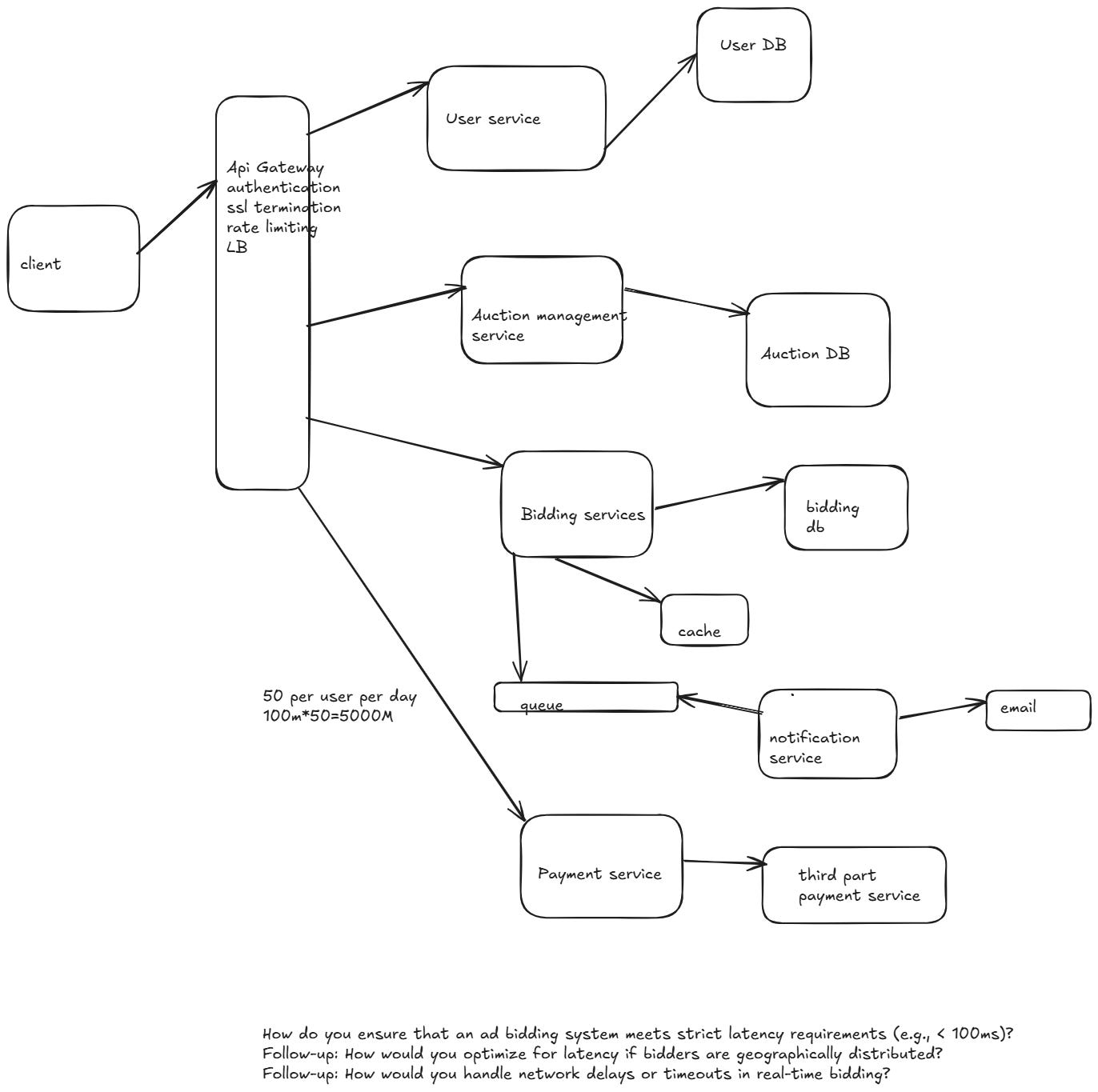
Design Ad bidding system
An Ad Bidding System is responsible for running real-time auctions for advertisements, allowing advertisers to bid for ad slots on platforms such as websites, mobile apps, and search engines
FR
1.The system should execute auctions in real-time, typically within a few milliseconds (e.g., 100ms or less) to avoid delays in serving ads.
2.Bids from advertisers must be evaluated, and a winner selected based on the highest bid and relevance.
3.Advertisers should be able to submit bids for specific ad slots (e.g., based on user demographics, location, keywords, or device type).
4.The system must validate the bids to ensure they meet constraints (e.g., minimum bids, campaign budgets)
5.Support for granular user targeting based on Demographics,geographic location,Behavioral data (e.g., browsing history, purchase intent),device type and OS
6.Track advertiser budgets and ensure that bids do not exceed the allocated budget.
for reports and anlytics enable near real-time and historical data views
NFR
1.System should be highly scalable to handle millions of bid requests per second (RPS) during peak traffic.
2.Ensure low-latency processing for bid requests to meet real-time requirements (<100ms).
3.The system should be highly available to avoid revenue loss during downtime.
4.System should be highly consistent
Estimates
Traffic Assumption
Requests per Second (RPS): 1 million.
Average Payload Size (bid request): 1 KB (including user data, ad slot details, etc.).
Average Response Size (bid response): 0.5 KB.
Daily Active Users (DAU): 100 million.
Average ads per user per day: 50.
Storage
User Profiles (for targeting):
100 million users × 1 KB per profile ≈ 100 GB.
Advertiser Campaign Data:
Assume 10,000 advertisers with campaigns averaging 10 KB each ≈ 100 MB.
Clickstream and Logs:
Average 50 clicks/user/day × 100 million users × 0.2 KB/click ≈ 1 TB/day of raw click data.API’s
1.POST api/v1/bid
Allow the ad exchange to send bid requests to bidders in real-time
request {
"auctionId": "123456",
"userId": "987654",
"adSlotId": "banner_1",
"device": {
"os": "Android",
"browser": "Chrome",
"ip": "192.168.0.1"
},
"context": {
"url": "https://example.com/article",
"keywords": ["sports", "football"]
},
"minBidPrice": 0.50
}
response
{
"auctionId": "123456",
"bidPrice": 1.25,
"adCreativeId": "creative_123",
"adUrl": "https://example.com/ad",
"targetingData": {
"region": "US",
"device": "Mobile"
}
}
2.POST api/v1/campaigns
Allow advertisers to create and manage their campaigns.
request {
"advertiserId": "7891011",
"budget": 1000,
"bidPrice": 1.0,
"targeting": {
"location": ["US", "CA"],
"ageGroup": "18-34",
"keywords": ["sports", "tech"]
},
"adCreatives": [
{
"creativeId": "creative_123",
"url": "https://example.com/ad",
"size": "300x250"
}
]
}
reponse
{
"campaignId": "456789",
"status": "created"
}
3.Update Campaign:PUT api/v1/campaigns/{campaignId}
4.Get Campaign Details:GET api/v1/campaigns/{campaignId}
5.GET /users/{userId}
Retrieve and update user profiles for targeting.
response {
"userId": "987654",
"interests": ["sports", "technology"],
"location": "US",
"ageGroup": "25-34",
"deviceHistory": [
{"os": "iOS", "browser": "Safari"},
{"os": "Android", "browser": "Chrome"}
]
}
6.POST api/v1/auction/results
request {
"auctionId": "123456",
"winnerBidderId": "bidder_001",
"winningBidPrice": 1.25,
"adCreativeId": "creative_123",
"adUrl": "https://example.com/ad"
}
response {
"status": "success"
}
7.GET api/v1/analytics/campaigns/{campaignId}
Provide reports on campaign performance and user engagement.
{
"campaignId": "456789",
"impressions": 100000,
"clicks": 5000,
"spend": 750.00,
"CTR": 0.05
}
8.POST api/v1/clickstream
request {
"eventId": "event_123",
"userId": "987654",
"adCreativeId": "creative_123",
"timestamp": "2024-12-21T10:20:30Z",
"action": "click",
"metadata": {
"url": "https://example.com/article",
"device": "Android",
"location": "US"
}
}
response
{
"status": "success"
}
Databases
1. Relational Database (SQL)
Purpose:
To store critical transactional data such as campaigns, bids, users, and auctions.
Enforce ACID properties for consistency and integrity.
Suitable for structured data with complex relationships.
Database: PostgreSQL, MySQL, or similar SQL databases.
Example Schemas:
Campaigns Table:
CREATE TABLE campaigns (
campaign_id SERIAL PRIMARY KEY,
advertiser_id INT NOT NULL,
budget DECIMAL(10, 2) NOT NULL,
bid_price DECIMAL(10, 2) NOT NULL,
targeting JSONB NOT NULL, -- For flexible targeting rules
status VARCHAR(20) DEFAULT 'active',
created_at TIMESTAMP DEFAULT CURRENT_TIMESTAMP,
updated_at TIMESTAMP DEFAULT CURRENT_TIMESTAMP
);
Bids Table
CREATE TABLE bids (
bid_id SERIAL PRIMARY KEY,
auction_id INT NOT NULL,
campaign_id INT NOT NULL,
bid_price DECIMAL(10, 2) NOT NULL,
ad_creative_id INT NOT NULL,
created_at TIMESTAMP DEFAULT CURRENT_TIMESTAMP
);
Users Table
CREATE TABLE users (
user_id SERIAL PRIMARY KEY,
location VARCHAR(50),
age_group VARCHAR(20),
interests JSONB,
created_at TIMESTAMP DEFAULT CURRENT_TIMESTAMP
);
2. NoSQL Database (Document Store)
Purpose:
Store unstructured or semi-structured data, such as user profiles and clickstream data.
Handle high read/write throughput with low latency.
Flexible schema for rapidly evolving data.
Database: MongoDB, DynamoDB, or Couchbase.
Example Schemas:
User Profiles Collection:
{
"_id": "987654",
"location": "US",
"age_group": "25-34",
"interests": ["sports", "technology"],
"device_history": [
{"os": "iOS", "browser": "Safari"},
{"os": "Android", "browser": "Chrome"}
],
"created_at": "2024-12-21T10:20:30Z"
}
click Stream collection
{
"event_id": "event_123",
"user_id": "987654",
"ad_creative_id": "creative_123",
"timestamp": "2024-12-21T10:20:30Z",
"action": "click",
"metadata": {
"url": "https://example.com/article",
"device": "Android",
"location": "US"
}
}
3. Key-Value Store
Purpose:
Cache frequently accessed data (e.g., user profiles, bidding rules) for low-latency reads.
Provide fast lookups for user targeting data or ad creatives.
Database: Redis, Memcached, or DynamoDB (in key-value mode).
Example Schemas:
Ad Creative Cache:
Key Value
creative_123 { "url": "https://example.com/ad", "size": "300x250" }
user_987654_interests ["sports", "technology"]
4. Time-Series Database
Purpose:
Store and analyze time-stamped data, such as impressions, clicks, or revenue trends over time.
Optimized for aggregations, time-window queries, and historical reporting.
Database: InfluxDB, TimescaleDB, or OpenTSDB.
Example Schemas:
Impressions Table (TimescaleDB):
CREATE TABLE impressions (
timestamp TIMESTAMPTZ NOT NULL,
ad_creative_id INT NOT NULL,
user_id INT,
device_type VARCHAR(20),
region VARCHAR(20),
impressions_count INT
);
Clicks table
CREATE TABLE clicks (
timestamp TIMESTAMPTZ NOT NULL,
ad_creative_id INT NOT NULL,
user_id INT,
click_count INT,
metadata JSONB
);
5. Analytical Database (OLAP)
Purpose:
Perform complex analytical queries for reporting and insights, such as ROI analysis, campaign performance, and fraud detection.
Store aggregated data and run queries over large data sets efficiently.
Database: Snowflake, Google BigQuery, Apache Druid, or ClickHouse.
Example Schemas:
Campaign Performance Table:
CREATE TABLE campaign_performance (
campaign_id INT,
date DATE,
impressions INT,
clicks INT,
spend DECIMAL(10, 2),
revenue DECIMAL(10, 2),
CTR DECIMAL(5, 4),
ROI DECIMAL(5, 4)
);
Fraud detection data table
CREATE TABLE campaign_performance (
campaign_id INT,
date DATE,
impressions INT,
clicks INT,
spend DECIMAL(10, 2),
revenue DECIMAL(10, 2),
CTR DECIMAL(5, 4),
ROI DECIMAL(5, 4)
);
6. Distributed Log Storage (Event Streaming)
Purpose:
Handle real-time message streams for bidding requests, events, and results.
Enable reliable, ordered event delivery for auction processes.
Database: Apache Kafka, Amazon Kinesis.
Example Topics and Schemas:
Bidding Requests Topic:
{
"auctionId": "123456",
"userId": "987654",
"adSlotId": "banner_1",
"minBidPrice": 0.50,
"timestamp": "2024-12-21T10:15:30Z"
}
Auction Results Topic:
{
"auctionId": "123456",
"winningBid": {
"bidderId": "bidder_001",
"bidPrice": 1.25,
"adCreativeId": "creative_123"
},
"timestamp": "2024-12-21T10:16:00Z"
}
HLD