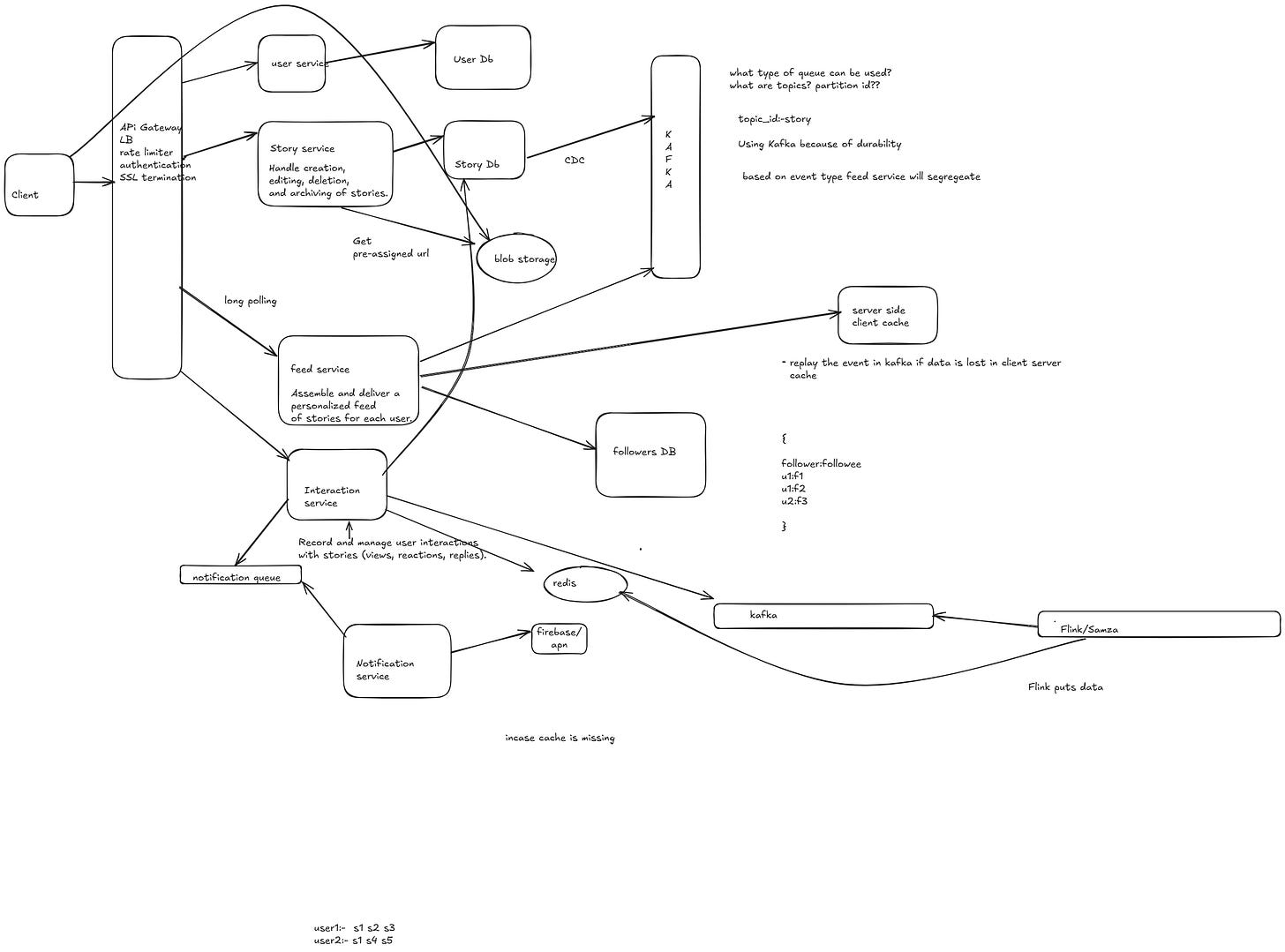
Design Instagram/whatsapp story
Designing Instagram Stories involves various functional requirements to ensure a smooth and engaging user experience. Here’s a breakdown of the key functional requirements:
FR
1.Users should be able to create a new story by capturing a photo, video, or uploading from the gallery.
2.Support for text-only stories with customizable fonts, colors, and backgrounds.
3.Support for stickers, GIFs, and emojis.
4.Ability to add music from a library or external sources.
5.Support for tagging other users (@mentions).
6.Ability to add hashtags and location tags.
7.Stories automatically expire after 24 hours
8.Users get notified when someone replies to their story.
9.Add/remove people from viewing story
10.Number of views/likes for given story
NFR
1.Minimal latency during story creation, publishing, and viewing, especially when applying filters or effects.
2.Ability to support high numbers of simultaneous users, especially during peak usage times.
3.System should be highly scalable to accommodate growth in the number of users and the volume of stories created.
4.System should be highly available (e.g., 99.9% availability) to ensure users can access and interact with stories anytime.
Estimates
Daily Active Users (DAU): 500 million
Percentage Posting Stories: ~10% of DAU → 50 million stories created per day
Average Story Size: ~3 MB (averaging between photos, videos, filters, etc.)
Average Stories Viewed per User: ~5 stories
Total Story Views: 500M users × 5 stories = 2.5 billion views per day
QPS=2.5B/10^5=25k QPSStorage
50 million stories × 3 MB = 150 million MB = 150 TB per day
API’s
1.POST /api/stories
request {
"userId": "user_123",
"mediaUrl": "https://cdn.example.com/media/abc123.jpg",
"mediaType": "image",
"filters": ["vintage"],
"stickers": [{ "type": "emoji", "position": { "x": 50, "y": 100 } }],
"location": "New York, NY",
"tags": ["#fun", "#travel"],
"createdAt": "2025-02-13T12:34:56Z"
"included_users":[id1,id2...],
"excluded_users":[id3,id4..]
}
2.PUT /api/stories/{storyId}
{
"filters": ["vintage", "contrast"],
"stickers": [{ "type": "emoji", "position": { "x": 60, "y": 110 } }]
}
3.DELETE /api/stories/{storyId}
4.GET /api/stories/feed
5.POST /api/stories/{storyId}/reactions
{
"userId": "user_456",
"reaction": "❤️", // or "textReply": "Awesome story!"
"timestamp": "2025-02-13T12:45:00Z"
}
6.POST /api/stories/{storyId}/share
{
"platform": "facebook",
"userId": "user_456",
"message": "Check out this story!"
}
7.POST /api/upload/media
{
"userId": "user_123",
"file": "<binary data>",
"mediaType": "video"
}
Databases
1. Relational Database Schema (e.g., PostgreSQL/MySQL)
Users Table
CREATE TABLE users (
user_id UUID PRIMARY KEY,
username VARCHAR(255) UNIQUE NOT NULL,
email VARCHAR(255) UNIQUE NOT NULL,
full_name VARCHAR(255),
profile_pic VARCHAR(1024),
created_at TIMESTAMP DEFAULT CURRENT_TIMESTAMP
);
Stories Table
CREATE TABLE stories (
story_id UUID PRIMARY KEY,
user_id UUID REFERENCES users(user_id),
media_url VARCHAR(1024) NOT NULL,
media_type VARCHAR(50) CHECK (media_type IN ('image', 'video', 'text')),
created_at TIMESTAMP DEFAULT CURRENT_TIMESTAMP,
expires_at TIMESTAMP,
privacy_setting VARCHAR(50) CHECK (privacy_setting IN ('public', 'close_friends', 'custom')),
filters JSONB,
stickers JSONB,
location VARCHAR(255),
tags JSONB,
archived BOOLEAN DEFAULT FALSE
);
Story Interactions Table
CREATE TABLE story_interactions (
interaction_id UUID PRIMARY KEY,
story_id UUID REFERENCES stories(story_id),
user_id UUID REFERENCES users(user_id),
interaction_type VARCHAR(50) CHECK (interaction_type IN ('emoji', 'text_reply', 'gif')),
value VARCHAR(1024),
created_at TIMESTAMP DEFAULT CURRENT_TIMESTAMP
);
Story Viewers Table
CREATE TABLE story_viewers (
view_id UUID PRIMARY KEY,
story_id UUID REFERENCES stories(story_id),
user_id UUID REFERENCES users(user_id),
viewed_at TIMESTAMP DEFAULT CURRENT_TIMESTAMP
);
Notifications Table
CREATE TABLE notifications (
notification_id UUID PRIMARY KEY,
user_id UUID REFERENCES users(user_id),
story_id UUID REFERENCES stories(story_id),
type VARCHAR(50) CHECK (type IN ('story_reply', 'new_view', 'reaction')),
message VARCHAR(1024),
read BOOLEAN DEFAULT FALSE,
created_at TIMESTAMP DEFAULT CURRENT_TIMESTAMP
);
2. NoSQL / Key-Value Store (e.g., Cassandra, DynamoDB, Redis)
Example: User Feed Document
{
"user_id": "user_123",
"stories_feed": [
{
"story_id": "story_456",
"media_url": "https://cdn.example.com/media/story_456.jpg",
"created_at": "2025-02-13T12:34:56Z",
"user_info": {
"username": "john_doe",
"profile_pic": "https://cdn.example.com/profiles/john.jpg"
}
}
// Additional story objects...
]
}
3. Analytics / Time-Series Schema (e.g., InfluxDB, TimescaleDB)
Story Metrics Table
CREATE TABLE story_metrics (
story_id UUID,
metric_timestamp TIMESTAMP,
views_count INTEGER,
reactions_count INTEGER,
tap_forward INTEGER,
tap_back INTEGER,
exits INTEGER,
PRIMARY KEY (story_id, metric_timestamp)
);
4. Blob Storage for Media Assets
Media Files: Use a blob storage service (like Amazon S3 or Google Cloud Storage).
Reference: The
media_urlfield in the Stories table stores the URL/path to the media file.
HLD