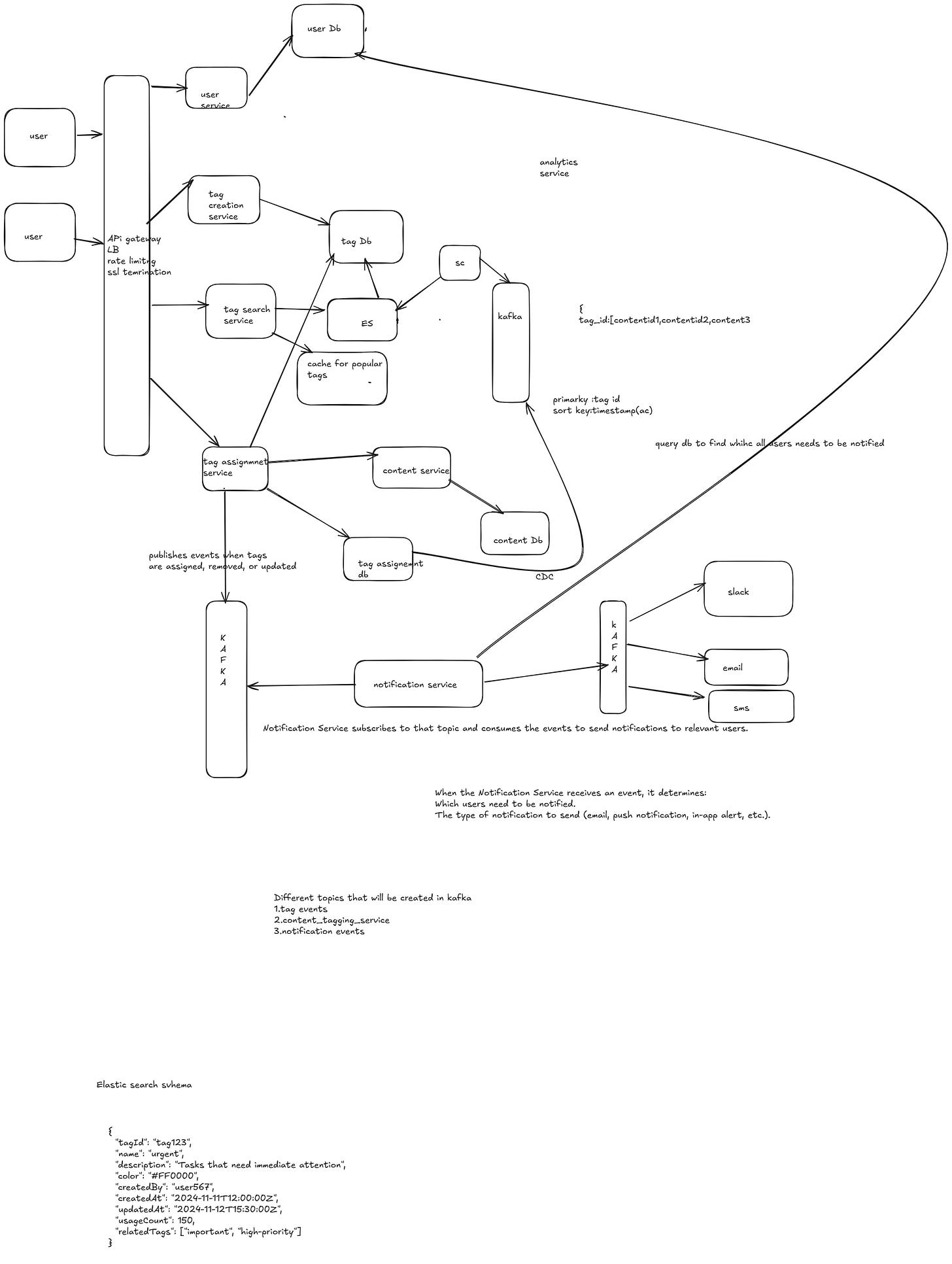
Design Tag management system
General Tag Management System that is flexible enough to integrate with various tools like project management platforms, content management systems, or other applications
FR
1.Users should be able to create new tags with unique names.
2. Users can edit tag details (name, description, color) or delete tags if they are no longer needed.
3. Users can assign one or more tags
to various types of content (e.g., documents, tasks, tickets, pages).
4.Tag suggestions should be provided based on frequently used or related tags
5.Users should be able to search for content using tags.
6.Get the top k tags
7.Search made on multiple tags??
NFR
1. System should be highly scalable to handle large number of tags and content without slowdowns.
2. Ensure high availability, especially if integrated with critical systems.
3.Low latency while searching for tags
4. Protect tag data and enforce access control from security purpose
Estimates
The system supports a large user base (e.g., enterprises, SaaS platforms).
Assume there are 10 million content items tagged.
Assume 1 million unique tags in the system.
On average, each content item has 3 tags assigned to itQPS
Assume 1 million users.
Peak Usage: 5% of users are active simultaneously during peak hours.
Average Requests per User: 2 tag-related actions per minute during peak usage.
DAU=10% of 1M=10^5
request per user per sec=2/60
total qps=10^5*2/60(100)=2k qpsStorage
Tag table
tag_id (UUID): 16 bytes
name (string): 50 bytes (average)
description (string): 100 bytes (average)
color (string): 10 bytes
created_at, updated_at (timestamps): 16 bytes
Total per tag: ~200 bytes
total storage=1M*200bytes=200MBTag assignment table
assignment_id (UUID): 16 bytes
content_id (UUID): 16 bytes
tag_id (UUID): 16 bytes
Total per assignment: ~50 bytes
Estimated 10 million content items with an average of 3 tags per item.
total tag assigment=10M∗3 tags/item=30M assignments.
storage= 30M*50=1500MB
total storage=200+1500=2GB
Search Qps
1 million users total.
10% of users are active during peak hours.
2 tag searches per minute per active user.
DAU=10%of 1M=10^5
Qps=10^5*2/60(100)=2k qps
API’s
1.POST /api/tags
Create a new tag with a unique name.
Request
{
"name": "project-management",
"description": "Tags related to project management",
"color": "#FF5733"
}
repsonse
{
"tagId": "123e4567-e89b-12d3-a456-426614174000",
"message": "Tag created successfully"
}
PUT /api/tags/{tagId}
Description: Update details of an existing tag.
request { "name": "project-management-updated", "description": "Updated description", "color": "#00FF00" } response { "message": "Tag updated successfully" }Endpoint:
DELETE /api/tags/{tagId}Description: Delete a tag by its ID.
{ "message": "Tag deleted successfully" }4.GET /api/tags
Retrieve a list of all tags.
[ { "tagId": "123e4567-e89b-12d3-a456-426614174000", "name": "project-management", "description": "Tags related to project management", "color": "#FF5733" } ]5.POST /api/content/{contentId}/tags
Assign multiple tags to a content item.
request { "tags": ["tagId1", "tagId2", "tagId3"] } response { "message": "Tags assigned to content successfully" }
6.DELETE /api/content/{contentId}/tagsRemove tags from a content item.
request { "tags": ["tagId1", "tagId2"] } response { "message": "Tags removed from content successfully" }7.GET /api/content/{contentId}/tags
Retrieve all tags assigned to a specific content item.
response [ { "tagId": "tagId1", "name": "urgent" } ]8.GET /api/search
Search for content based on tags.
Query Params:
tags=tagId1,tagId[ { "contentId": "456e4567-e89b-12d3-a456-426614174111", "title": "Project Plan", "tags": ["project-management", "planning"] } ]9.Endpoint: GET /api/tags/top?limit=5
Description: Retrieve the most frequently used tags.
Query Params:
limit=5[ { "tagId": "tagId1", "name": "urgent", "usageCount": 150 } ]10.GET /api/tags/suggestions
Suggest tags based on partially entered text or related tags.
Query Params:
query=proj[ { "tagId": "tagId2", "name": "project-management" }, { "tagId": "tagId3", "name": "project-planning" } ]Database Schema
1.Tags table
CREATE TABLE tags ( tag_id UUID PRIMARY KEY DEFAULT gen_random_uuid(), name VARCHAR(100) UNIQUE NOT NULL, description TEXT, color VARCHAR(7), -- e.g., "#FF5733" created_at TIMESTAMP DEFAULT NOW(), updated_at TIMESTAMP DEFAULT NOW() );2.Content Table
CREATE TABLE content ( content_id UUID PRIMARY KEY DEFAULT gen_random_uuid(), title VARCHAR(255) NOT NULL, body TEXT, content_type VARCHAR(50), -- e.g., "document", "ticket", "task" created_at TIMESTAMP DEFAULT NOW(), updated_at TIMESTAMP DEFAULT NOW() );3.
Tag_assignmentsTableThis table manages the many-to-many relationship between tags and content. It allows multiple tags to be assigned to a single content item and vice versa. CREATE TABLE tag_assignments ( assignment_id UUID PRIMARY KEY DEFAULT gen_random_uuid(), content_id UUID NOT NULL, tag_id UUID NOT NULL, assigned_at TIMESTAMP DEFAULT NOW(), FOREIGN KEY (content_id) REFERENCES content(content_id) ON DELETE CASCADE, FOREIGN KEY (tag_id) REFERENCES tags(tag_id) ON DELETE CASCADE, UNIQUE (content_id, tag_id) );4.
tag_analyticsTableCREATE TABLE tag_analytics ( tag_id UUID PRIMARY KEY, usage_count INT DEFAULT 0, last_used_at TIMESTAMP, FOREIGN KEY (tag_id) REFERENCES tags(tag_id) ON DELETE CASCADE );Relationship among tables
Tags and Content: Many-to-many relationship managed by the tag_assignments table. Each content item can have multiple tags, and each tag can be assigned to multiple content items. Tag Analytics: Tracks the usage statistics of tags based on assignments in the tag_assignments table.
Optimizing for High QPS in Search
To efficiently handle a high search QPS, the system would need optimizations such as:
Indexing: Using tools like Elasticsearch or Solr to quickly search through tags and associated content.
Caching: Caching frequently searched tags and results using systems like RedisHL